Flooded Batteries Vs. Lead Acid Batteries
Contents
- 1 Flooded Batteries Vs. Lead Acid Batteries
- 2 Flooded Batteries: What to Know?
- 3 Daily Applications of Flooded Batteries
- 3.1 1. Automotive Starting Batteries:
- 3.2 2. Backup Power Systems:
- 3.3 3. Marine Applications:
- 3.4 4. Golf Carts and Electric Vehicles:
- 3.5 5. Solar Energy Systems:
- 3.6 6. Recreational Vehicles (RVs):
- 3.7 7. Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS):
- 3.8 8. Electric Fences:
- 3.9 9. Emergency Lighting:
- 3.10 10. Remote Monitoring and Telemetry Systems:
- 3.11 11. Wheelchairs and Mobility Scooters:
- 3.12 12. Standby Generators:
- 4 Lead Acid Batteries: A Basic Guide
- 5 Everyday Applications of Lead Acid Batteries
- 5.1 1. Automotive Batteries:
- 5.2 2. Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS):
- 5.3 3. Emergency Lighting:
- 5.4 4. Marine Batteries:
- 5.5 5. RV and Camper Batteries:
- 5.6 6. Golf Cart Batteries:
- 5.7 7. Motorized Wheelchairs and Mobility Scooters:
- 5.8 8. Solar Energy Systems:
- 5.9 9. Electric Bicycles:
- 5.10 10. Standby Generators:
- 5.11 11. Electric Scooters:
- 5.12 12. Alarm and Security Systems:
- 5.13 13. Aircraft and Aviation:
- 5.14 14. Medical Equipment:
- 5.15 15. Forklifts:
- 5.16 16. Utility and Telecommunication Backup:
- 5.17 17. Electric Gates and Garage Door Openers:
- 5.18 18. Sump Pumps:
- 5.19 19. Recreational Boats:
- 6 Conclusion
- 7 FAQ

Batteries are integral to our daily lives, powering everything from our cars to our portable devices. When it comes to more extensive energy storage needs, flooded batteries and lead-acid batteries are two standard options. This article will explore the differences between Flooded Batteries Vs. Lead Acid Batteries. These two battery types help you decide which fits your requirements best.
Flooded Batteries: What to Know?

Flooded batteries, also known as wet cell batteries, are a type of lead-acid battery. They are called “flooded” because they contain a liquid electrolyte, typically a mixture of water and sulfuric acid. Here are some key points to understand about flooded batteries:
1. Chemical Reaction:
Flooded batteries generate electricity through a chemical reaction between the lead plates (positive and negative) and the electrolyte. This reaction creates electrical energy.
2. Maintenance:
Flooded batteries require regular maintenance. The water level in the cells needs to be monitored and topped up periodically because the electrolyte can evaporate over time. This maintenance involves checking and replenishing the water to ensure the battery’s proper function.
3. Cost-Effective:
Flooded batteries are often the most cost-effective option in the lead acid battery category. They are relatively affordable compared to other battery types, making them a popular choice for budget-conscious consumers.
4. Energy Efficiency:
Flooded batteries are known for their high energy efficiency. They can deliver a substantial amount of power quickly, which makes them suitable for applications that require bursts of energy, such as starting a car or operating power backup systems.
5. Lifespan:
The lifespan of a flooded battery can vary depending on factors like usage, maintenance, and quality. With proper care, flooded batteries can last several years.
Daily Applications of Flooded Batteries

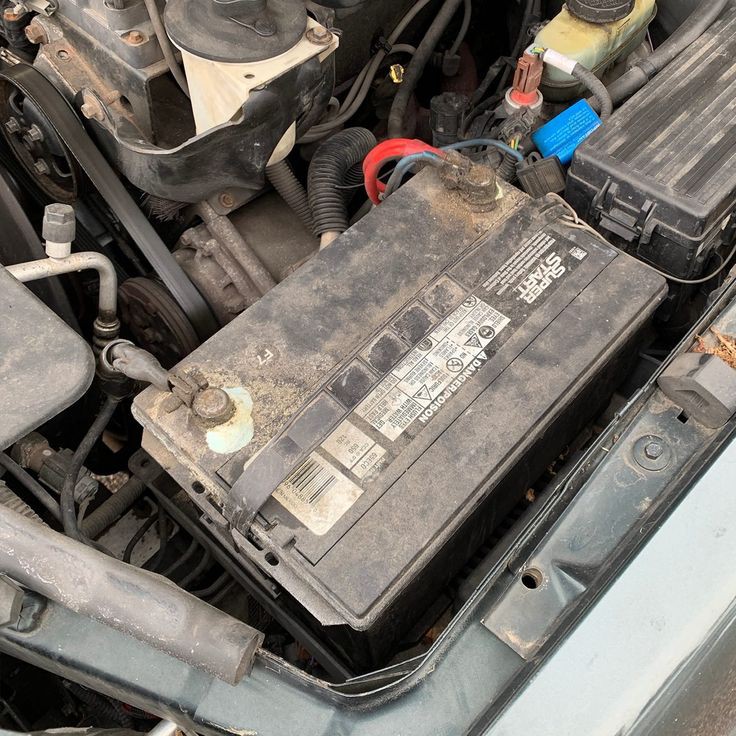
1. Automotive Starting Batteries:
Flooded batteries are widely used as starting batteries in automobiles, motorcycles, trucks, and other vehicles. They provide the initial burst of energy required to start the engine.
2. Backup Power Systems:
Many homes and businesses use flooded batteries as backup power systems. These batteries store energy and can provide electricity during power outages, ensuring that essential appliances and equipment continue to operate.
3. Marine Applications:
Flooded batteries are commonly found in boats and marine vehicles, which power various electrical components, including lights, radios, and navigation systems. They are ideal for marine use due to their cost-effectiveness.
4. Golf Carts and Electric Vehicles:
Flooded batteries are often used in golf carts and smaller electric vehicles like scooters. They offer a balance of performance and affordability for such applications.
5. Solar Energy Systems:
Flooded batteries store excess energy generated by solar panels in off-grid and grid-tied solar energy systems. This stored energy can be used at night during low solar production or cloudy days.
6. Recreational Vehicles (RVs):
Many RVs and campers use flooded batteries to power the onboard electrical systems, including lighting, refrigeration, and entertainment devices. They are a cost-effective solution for extended trips.
7. Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS):
Flooded batteries, commonly known as UPS systems, are also used in uninterruptible power supplies. These devices provide short-term power during electrical interruptions, protecting critical equipment in data centers and offices.
8. Electric Fences:
Flooded batteries in agricultural and rural settings power electric fences, which help contain livestock and protect crops from wildlife.
9. Emergency Lighting:
Flooded batteries are often employed in emergency lighting systems in commercial buildings, ensuring that exit signs and emergency lights function during power failures or emergencies.
10. Remote Monitoring and Telemetry Systems:
Flooded batteries ensure uninterrupted operation in remote locations with a constant power supply for monitoring and telemetry systems.
11. Wheelchairs and Mobility Scooters:
Flooded batteries can be found in electric wheelchairs and mobility scooters, providing the power needed for mobility and independence.
12. Standby Generators:
Some standby generators have flooded batteries to initiate startup when the primary power source fails. This ensures the generator can start and provide backup power as needed.
Lead Acid Batteries: A Basic Guide
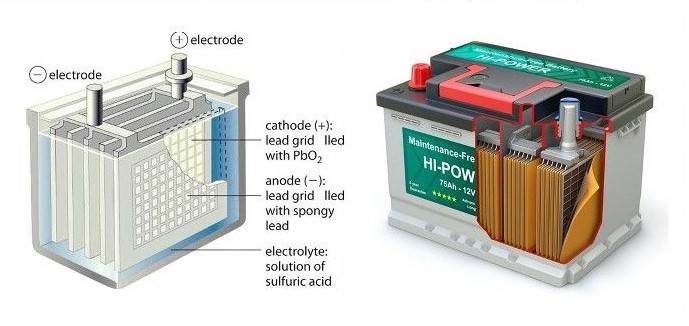
Lead acid batteries encompass various types, including flooded batteries. The use of lead-based electrodes and sulfuric acid electrolytes characterizes them. Here’s what you need to know about lead acid batteries in general:
1. Versatility:
Lead acid batteries are versatile and find application in various settings. They are commonly used to power vehicles (like cars, trucks, and motorcycles), provide backup power for homes and businesses, and support renewable energy systems, such as solar power storage.
2. Environmental Concerns:
Lead acid batteries, including flooded ones, have environmental concerns due to their lead content. Lead is a toxic heavy metal, and if not disposed of properly, it can lead to contamination of the environment. Recycling lead-acid batteries is essential to mitigate these environmental impacts.
3. Types of Lead Acid Batteries:
In addition to flooded batteries, lead acid batteries include absorbed glass mats (AGM) and gel batteries. AGM batteries are maintenance-free and sealed, while gel batteries use a gel-like electrolyte. These variations cater to different needs and preferences.
4. Charging and Discharging:
Lead acid batteries can be charged and discharged and can handle deep discharges without significant damage. This feature makes them suitable for applications that require a steady power supply over time.
5. Weight:
Lead acid batteries, including flooded ones, tend to be heavier than other battery types, affecting portability and installation in certain situations.
Everyday Applications of Lead Acid Batteries

Lead acid batteries, including various types such as flooded batteries, absorbed glass mat (AGM) batteries, and gel batteries, are widely used in everyday life due to their versatility and reliability. Here are typical regular applications where you can find lead acid batteries:
1. Automotive Batteries:
Lead acid batteries are the most common type used in cars, trucks, motorcycles, and other vehicles. They provide the initial burst of energy needed to start the engine and power various vehicle systems.
2. Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS):
Many homes and businesses use lead-acid batteries in UPS systems to ensure a continuous power supply during electrical outages, preventing data loss and equipment damage.
3. Emergency Lighting:
Lead acid batteries are used in emergency lighting systems in commercial buildings, ensuring that exit signs and emergency lights function during power failures or emergencies.
4. Marine Batteries:
Boats and marine vessels use lead-acid batteries to power navigation lights, radios, pumps, and other electrical equipment.
5. RV and Camper Batteries:
Lead acid batteries are commonly used in recreational vehicles (RVs) and campers to provide power for lighting, appliances, and entertainment systems.
6. Golf Cart Batteries:
Electric golf carts often use lead-acid batteries for propulsion and electrical systems.
7. Motorized Wheelchairs and Mobility Scooters:
Lead acid batteries power electric wheelchairs and mobility scooters, providing mobility and independence to individuals with mobility challenges.
8. Solar Energy Systems:
Off-grid and grid-tied solar energy systems use lead-acid batteries, including AGM and gel batteries, to store excess energy generated by solar panels for use during periods of low solar production.
9. Electric Bicycles:
Some electric bicycles (e-bikes) use lead-acid batteries to provide the electric assistance needed for pedaling.
10. Standby Generators:
Lead acid batteries are often used to start standby generators in homes and businesses. These batteries ensure the generator can create and provide backup power during outages.
11. Electric Scooters:
Shared electric scooters used for urban transportation often rely on lead-acid batteries for their power source.
12. Alarm and Security Systems:
Lead acid batteries are used in alarm and security systems to provide backup power for monitoring, alarms, and communication devices during power disruptions.
13. Aircraft and Aviation:
In aircraft, lead acid batteries are used for various purposes, including starting engines and powering onboard avionics.
14. Medical Equipment:
Lead acid batteries are used in various medical devices, such as portable X-ray machines, defibrillators, and emergency lighting in healthcare facilities.
15. Forklifts:
Industrial forklifts commonly use lead-acid batteries for power, as they can provide the high current required for lifting heavy loads.
16. Utility and Telecommunication Backup:
Lead acid batteries provide backup power for utility substations, telecommunication systems, and remote facilities.
17. Electric Gates and Garage Door Openers:
Lead acid batteries are used in automated gate and garage door opener systems to ensure smooth operation during power interruptions.
18. Sump Pumps:
Some sump pump systems use lead-acid batteries as a backup power source to prevent basement flooding during power outages.
19. Recreational Boats:
Small recreational boats and personal watercraft often use lead-acid batteries for starting engines and powering onboard electronics.
Conclusion
Flooded Batteries Vs. Lead Acid Batteries
Flooded batteries are a specific type of lead acid battery that uses a liquid electrolyte. They are known for their cost-efficiency and energy efficiency but require regular maintenance.
Lead acid batteries, in general, offer versatility and find application in various domains. Understanding the differences between these batteries can help you make an informed choice based on your needs and priorities.
FAQ

Flooded Batteries:
Q1. What is a flooded battery, and how does it work?
A flooded battery, or wet cell battery, is a lead-acid battery. It contains a liquid electrolyte, usually water and sulfuric acid. These batteries work through a chemical reaction between the lead plates (positive and negative) and the electrolyte. This chemical reaction generates electrical energy, powering various devices and systems.
Q2. What maintenance is required for flooded batteries?
Flooded batteries require regular maintenance to ensure their optimal performance and lifespan. The primary maintenance tasks include checking and maintaining the water level in the battery cells. The electrolyte can evaporate over time, leading to a decrease in battery performance. To maintain a flooded battery, periodically inspect the water level and add distilled water as needed. Additionally, it’s essential to keep the battery clean and free from corrosion on the terminals.
Lead Acid Batteries:
Q1. What are the different types of lead-acid batteries, and how do they differ?
Lead acid batteries come in various types, including flooded, absorbed glass mats (AGM) and gel batteries. These types differ primarily in their construction and electrolyte management:
Flooded Batteries:
These are the traditional wet cell batteries containing a liquid electrolyte. They require regular maintenance to check and top up the water level in the cells.
AGM Batteries:
AGM batteries are valve-regulated lead acid (VRLA) batteries that use a glass mat separator to hold the electrolyte. They are maintenance-free and sealed, making them ideal for applications where minimal maintenance is preferred.
Gel Batteries:
Gel batteries use a gel-like electrolyte, which immobilizes the acid. They are also maintenance-free and have enhanced resistance to vibration and deep discharges.
The choice among these types depends on the specific application and the user’s preferences for maintenance, sealed design, and performance characteristics.
Q2. Can lead acid batteries be recycled, and what are the environmental considerations?
Yes, lead-acid batteries are highly recyclable, and recycling them is beneficial and crucial for environmental reasons. Lead is a toxic heavy metal, and improperly disposed lead acid batteries can contaminate soil and water. Recycling lead acid batteries helps in:
Recovering Lead:
Recycling involves extracting lead from old batteries and reusing it to manufacture new ones. This reduces the need for mining and processing new lead, conserving natural resources.
Environmental Protection:
Proper recycling prevents lead leakage into the environment, which can harm ecosystems and human health.
Reducing Landfill Waste:
Recycling lead-acid batteries minimizes the number of batteries ending up in landfills, reducing environmental impact.
Many countries and regions have established recycling programs and regulations to ensure lead-acid batteries’ safe disposal and recycling. When replacing a lead acid battery, it must be disposed of at a designated recycling center or through a certified battery retailer to support responsible and eco-friendly battery disposal practices.







